-
Mon - Sat: 10:00am - 6:30pm
-
Medhavi, Lokhandwala Complex, Andheri West

Physiotherapy Treatments
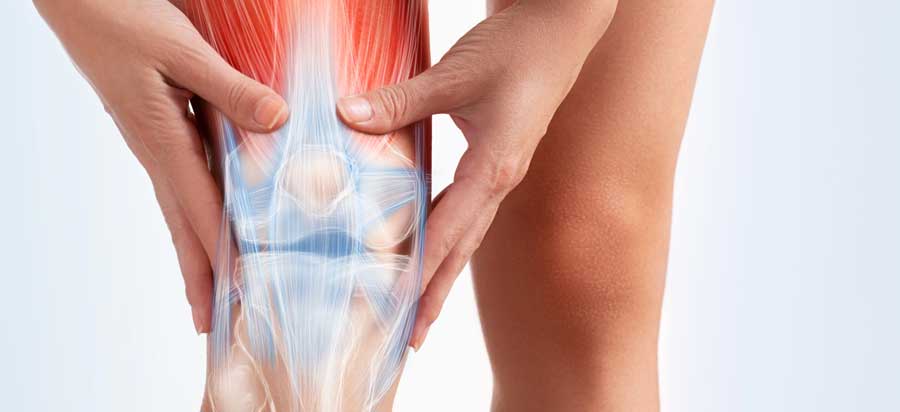
Osteoarthritis
Osteoarthritis is a degenerative joint disease in which the cartilage of the joints gradually wears away. This leads to joint pain, stiffness, and difficulty in movement. It most commonly affects the knees, hips, spine, and hand joints.
Common Symptoms
-
Joint pain during walking or movement
-
Stiffness in the morning or after periods of rest
-
Joint swelling and tenderness
-
Reduced range of motion
Goals of Physiotherapy
-
Reduce pain and stiffness
-
Improve joint mobility and flexibility
-
Strengthen muscles that support the joints
-
Enhance daily activities and overall quality of life
Physiotherapy Treatments
1. Pain Relief Techniques
-
Heat Therapy: Helps reduce joint stiffness and muscle tightness.
-
Cold Therapy: Used to reduce joint inflammation and swelling.
-
TENS Therapy: Used for pain control and muscle relaxation.
2. Range of Motion & Flexibility Exercises
-
Joint Mobility Exercises: Gentle movements for the knee, hip, or affected joint.
-
Stretching Exercises: To reduce muscle tightness.
-
Low-Impact Activities: Such as slow walking and cycling.
3. Strengthening Exercises
To improve joint support:
-
Quadriceps Strengthening: Essential for knee osteoarthritis.
-
Hip & Gluteal Exercises: Improve hip and lower limb stability.
-
TheraBand Exercises: Increase muscle strength using gradual resistance.
4. Manual Therapy
-
Gentle joint mobilization techniques performed by a physiotherapist.
-
Helps reduce joint stiffness and improve movement.
5. Lifestyle & Functional Training
-
Weight management and joint protection techniques.
-
Training for daily activities such as walking and stair climbing.
Frequency and Duration
-
Physiotherapy sessions are usually conducted 2–3 days per week.
-
A regular home exercise program is essential.
-
With long-term management, pain and mobility can be effectively controlled.
